Category:Jung Won KANG
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jung Won KANG
Executive Summary
Jung Won KANG is an inventor who has filed 2 patents. Their primary areas of innovation include by monitoring actual compressed data size at the memory before deciding storage at the transmission buffer (2 patents), the unit being an image region, e.g. an object (2 patents), among a plurality of spatial predictive coding modes (1 patents), and they have worked with companies such as Intellectual Discovery Co., Ltd. (1 patents), INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO., LTD. (1 patents). Their most frequent collaborators include (2 collaborations), (2 collaborations), (2 collaborations).
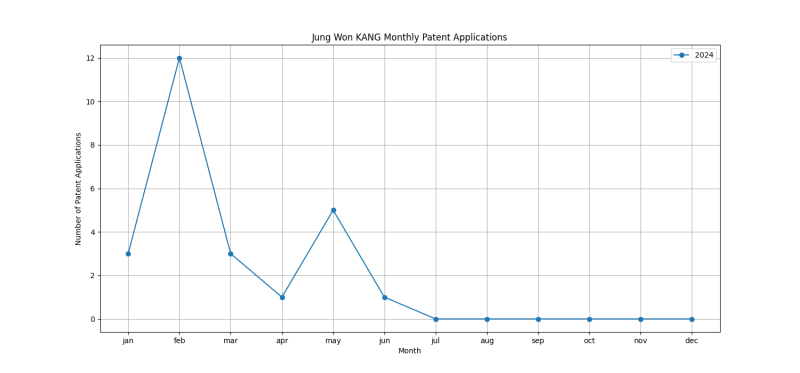
Patent Filing Activity
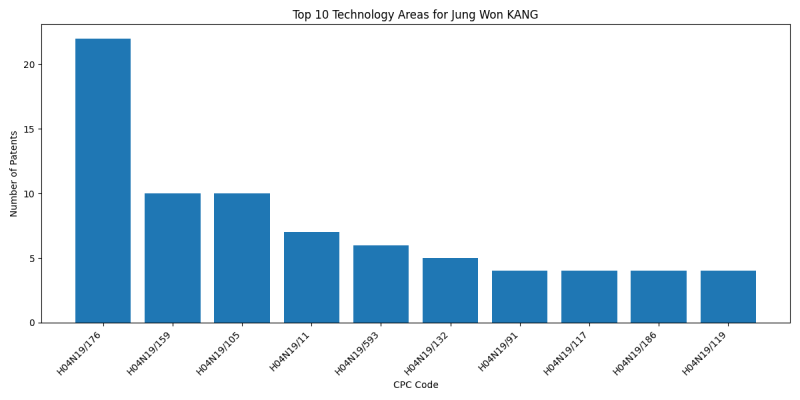
Technology Areas
List of Technology Areas
- H04N19/159 (by monitoring actual compressed data size at the memory before deciding storage at the transmission buffer): 2 patents
- H04N19/176 (the unit being an image region, e.g. an object): 2 patents
- H04N19/11 (among a plurality of spatial predictive coding modes): 1 patents
- H04N19/119 (Adaptive subdivision aspects, e.g. subdivision of a picture into rectangular or non-rectangular coding blocks): 1 patents
- H04N19/44 (Decoders specially adapted therefor, e.g. video decoders which are asymmetric with respect to the encoder): 1 patents
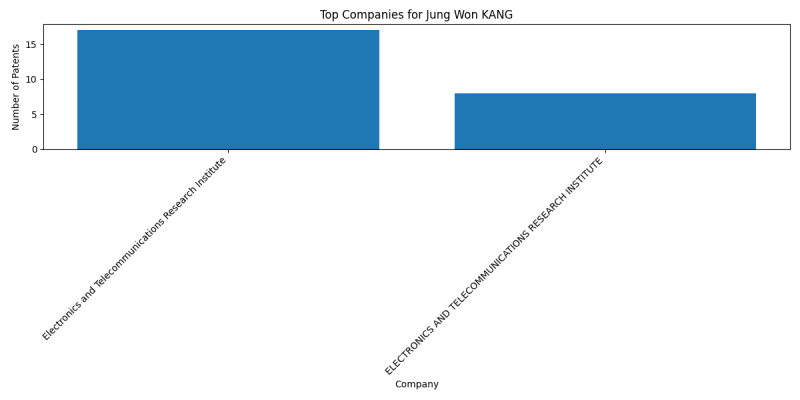
Companies
List of Companies
- Intellectual Discovery Co., Ltd.: 1 patents
- INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO., LTD.: 1 patents
Collaborators
- Dong San JUN (2 collaborations)
- Sung Chang LIM (2 collaborations)
- Hyun Suk KO (2 collaborations)
- Jin Ho LEE (2 collaborations)
- Ha Hyun LEE (2 collaborations)
- Hui Yong KIM (2 collaborations)
Subcategories
This category has the following 9 subcategories, out of 9 total.