Category:Hui Yong KIM
Contents
Hui Yong KIM
Executive Summary
Hui Yong KIM is an inventor who has filed 35 patents. Their primary areas of innovation include the unit being an image region, e.g. an object (30 patents), Selection of the reference unit for prediction within a chosen coding or prediction mode, e.g. adaptive choice of position and number of pixels used for prediction (15 patents), involving spatial prediction techniques (14 patents), and they have worked with companies such as Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (25 patents), ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS RESEARCH INSTITUTE (10 patents). Their most frequent collaborators include (34 collaborations), (34 collaborations), (29 collaborations).
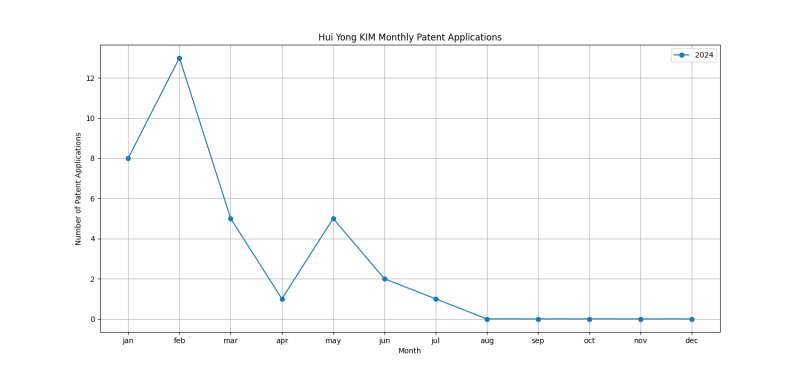
Patent Filing Activity
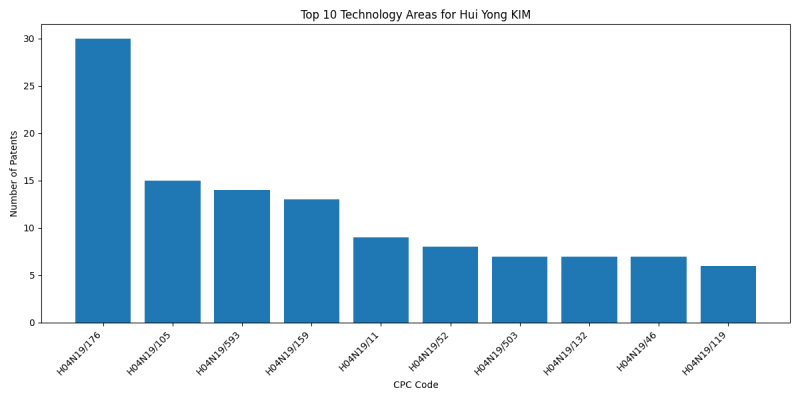
Technology Areas
List of Technology Areas
- H04N19/176 (the unit being an image region, e.g. an object): 30 patents
- H04N19/105 (Selection of the reference unit for prediction within a chosen coding or prediction mode, e.g. adaptive choice of position and number of pixels used for prediction): 15 patents
- H04N19/593 (involving spatial prediction techniques): 14 patents
- H04N19/159 (by monitoring actual compressed data size at the memory before deciding storage at the transmission buffer): 13 patents
- H04N19/11 (among a plurality of spatial predictive coding modes): 9 patents
- H04N19/52 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 8 patents
- H04N19/503 (involving temporal prediction (adaptive coding with adaptive selection between spatial and temporal predictive coding): 7 patents
- H04N19/132 (Sampling, masking or truncation of coding units, e.g. adaptive resampling, frame skipping, frame interpolation or high-frequency transform coefficient masking): 7 patents
- H04N19/46 (Embedding additional information in the video signal during the compression process (): 7 patents
- H04N19/119 (Adaptive subdivision aspects, e.g. subdivision of a picture into rectangular or non-rectangular coding blocks): 6 patents
- H04N19/136 (Adaptive entropy coding, e.g. adaptive variable length coding [AVLC] or context adaptive binary arithmetic coding [CABAC]): 5 patents
- H04N19/44 (Decoders specially adapted therefor, e.g. video decoders which are asymmetric with respect to the encoder): 5 patents
- H04N19/513 (Processing of motion vectors): 5 patents
- H04N19/91 (Entropy coding, e.g. variable length coding [VLC] or arithmetic coding): 4 patents
- H04N19/117 (Filters, e.g. for pre-processing or post-processing (sub-band filter banks): 4 patents
- H04N19/186 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 4 patents
- H04N19/182 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 4 patents
- H04N19/70 (characterised by syntax aspects related to video coding, e.g. related to compression standards): 4 patents
- H04N19/61 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 3 patents
- H04N19/139 (Analysis of motion vectors, e.g. their magnitude, direction, variance or reliability): 3 patents
- H04N19/1883 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 3 patents
- H04N19/184 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 3 patents
- H04N19/157 (Assigned coding mode, i.e. the coding mode being predefined or preselected to be further used for selection of another element or parameter): 3 patents
- H04N19/50 (using predictive coding (): 3 patents
- H04N19/96 (Tree coding, e.g. quad-tree coding): 3 patents
- H04N19/146 (Data rate or code amount at the encoder output): 3 patents
- H04N19/172 (the unit being an image region, e.g. an object): 3 patents
- H04N19/196 (being specially adapted for the computation of encoding parameters, e.g. by averaging previously computed encoding parameters (processing of motion vectors): 2 patents
- H04N19/167 (Position within a video image, e.g. region of interest [ROI]): 2 patents
- H04N19/12 (Selection from among a plurality of transforms or standards, e.g. selection between discrete cosine transform [DCT] and sub-band transform or selection between H.263 and H.264): 2 patents
- H04N19/18 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 2 patents
- H04N19/107 (between spatial and temporal predictive coding, e.g. picture refresh): 2 patents
- H04N19/137 (Motion inside a coding unit, e.g. average field, frame or block difference): 2 patents
- H04N19/82 (involving filtering within a prediction loop): 2 patents
- H04N19/147 (according to rate distortion criteria (rate-distortion as a criterion for motion estimation): 2 patents
- H04N19/13 (Adaptive entropy coding, e.g. adaptive variable length coding [AVLC] or context adaptive binary arithmetic coding [CABAC]): 2 patents
- H04N19/103 (using adaptive coding): 2 patents
- H04N19/109 (among a plurality of temporal predictive coding modes): 2 patents
- H04N19/577 (Motion compensation with bidirectional frame interpolation, i.e. using B-pictures): 2 patents
- H04N19/129 (Scanning of coding units, e.g. zig-zag scan of transform coefficients or flexible macroblock ordering [FMO]): 2 patents
- H04N19/124 (Quantisation): 2 patents
- H04N19/10 (using adaptive coding): 1 patents
- H04N19/197 (using optimisation based on Lagrange multipliers): 1 patents
- H04N19/127 (Prioritisation of hardware or computational resources): 1 patents
- G06T9/004 ({Predictors, e.g. intraframe, interframe coding}): 1 patents
- H04N19/189 (characterised by the adaptation method, adaptation tool or adaptation type used for the adaptive coding): 1 patents
- H04N19/517 (Motion estimation or motion compensation): 1 patents
- H04N19/597 (specially adapted for multi-view video sequence encoding): 1 patents
- H04N19/169 (characterised by the coding unit, i.e. the structural portion or semantic portion of the video signal being the object or the subject of the adaptive coding): 1 patents
- H04N19/51 (Motion estimation or motion compensation): 1 patents
- H04N19/57 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 1 patents
- H04N19/619 ({the transform being operated outside the prediction loop}): 1 patents
- H04N19/56 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 1 patents
- H04N19/149 (by estimating the code amount by means of a model, e.g. mathematical model or statistical model): 1 patents
- H04N19/17 (the unit being an image region, e.g. an object): 1 patents
- H04N19/174 (the region being a slice, e.g. a line of blocks or a group of blocks): 1 patents
- H04N19/192 (the adaptation method, adaptation tool or adaptation type being iterative or recursive): 1 patents
- H04N19/55 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 1 patents
- H04N19/563 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 1 patents
- H04N19/122 (Selection of transform size, e.g. 8x8 or 2x4x8 DCT; Selection of sub-band transforms of varying structure or type): 1 patents
- H04N19/625 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 1 patents
- H04N19/30 (using hierarchical techniques, e.g. scalability (): 1 patents
- H04N19/126 (Details of normalisation or weighting functions, e.g. normalisation matrices or variable uniform quantisers): 1 patents
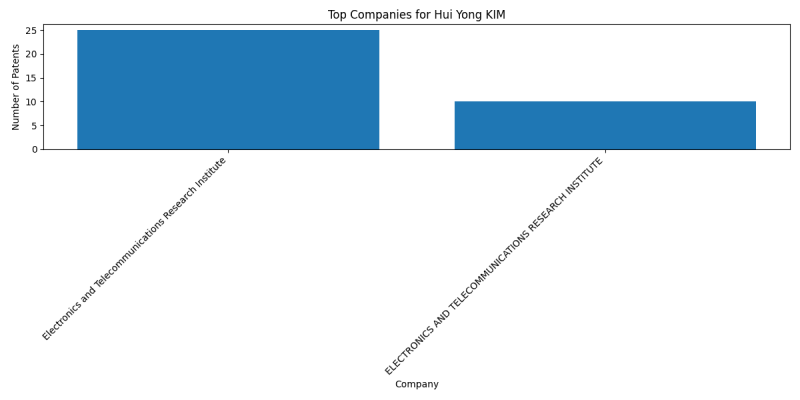
Companies
List of Companies
- Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute: 25 patents
- ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS RESEARCH INSTITUTE: 10 patents
Collaborators
- Sung Chang LIM (34 collaborations)
- Jin Ho LEE (34 collaborations)
- Ha Hyun LEE (29 collaborations)
- Jung Won KANG (21 collaborations)
- Jin Soo CHOI (18 collaborations)
- Jin Woong KIM (13 collaborations)
- Gwang Hoon PARK (10 collaborations)
- Hyun Suk KO (9 collaborations)
- Dong San JUN (9 collaborations)
- Jong Ho KIM (8 collaborations)
- Se Yoon JEONG (7 collaborations)
- Kyung Yong KIM (6 collaborations)
- Yung Lyul LEE (5 collaborations)
- Dae Yeon KIM (5 collaborations)
- Suk Hee CHO (5 collaborations)
- Seung Hyun CHO (5 collaborations)
- Jae Gon KIM (4 collaborations)
- Hae Chul CHOI (4 collaborations)
- Chie Teuk AHN (3 collaborations)
- Tae Hyun KIM (3 collaborations)
- Sang Min KIM (3 collaborations)
- Ji Yeon JUNG (2 collaborations)
- Nam Uk KIM (2 collaborations)
- Myung Jun KIM (2 collaborations)
- Yang Woo KIM (2 collaborations)
- Dae Young LEE (2 collaborations)
- Jin Woo HONG (2 collaborations)
- Dong Gyu SIM (2 collaborations)
- Seoung Jun OH (2 collaborations)
- Dong Jin PARK (2 collaborations)
- Do Hyeon PARK (2 collaborations)
- Tae Ryong KIM (1 collaborations)
- Han Soo LEE (1 collaborations)
- Gun BANG (1 collaborations)
- Woo Woen GWUN (1 collaborations)
- Won Jun LEE (1 collaborations)
- Dae Hyeok GWON (1 collaborations)
- Myoung Hun JANG (1 collaborations)
- Wook Je JEONG (1 collaborations)
- Ji Hoon DO (1 collaborations)
- Yong Uk YOON (1 collaborations)
- Byeung Woo JEON (1 collaborations)
- Jee Yoon PARK (1 collaborations)
- Sang Yong LEE (1 collaborations)
- Un Ki PARK (1 collaborations)
- Jun Woo CHOI (1 collaborations)
- Sea Nae PARK (1 collaborations)
- Chan Woong JEON (1 collaborations)
Subcategories
This category has the following 8 subcategories, out of 8 total.
G
H
J
S
- Sung Chang LIM
- Jin Ho LEE
- Ha Hyun LEE
- Jung Won KANG
- Jin Soo CHOI
- Jin Woong KIM
- Gwang Hoon PARK
- Hyun Suk KO
- Dong San JUN
- Jong Ho KIM
- Se Yoon JEONG
- Kyung Yong KIM
- Yung Lyul LEE
- Dae Yeon KIM
- Suk Hee CHO
- Seung Hyun CHO
- Jae Gon KIM
- Hae Chul CHOI
- Chie Teuk AHN
- Tae Hyun KIM
- Sang Min KIM
- Ji Yeon JUNG
- Nam Uk KIM
- Myung Jun KIM
- Yang Woo KIM
- Dae Young LEE
- Jin Woo HONG
- Dong Gyu SIM
- Seoung Jun OH
- Dong Jin PARK
- Do Hyeon PARK
- Tae Ryong KIM
- Han Soo LEE
- Gun BANG
- Woo Woen GWUN
- Won Jun LEE
- Dae Hyeok GWON
- Myoung Hun JANG
- Wook Je JEONG
- Ji Hoon DO
- Yong Uk YOON
- Byeung Woo JEON
- Jee Yoon PARK
- Sang Yong LEE
- Un Ki PARK
- Jun Woo CHOI
- Sea Nae PARK
- Chan Woong JEON
- Hui Yong KIM
- Inventors
- Inventors filing patents with Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute
- Inventors filing patents with ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS RESEARCH INSTITUTE