Category:Jizheng Xu of San Diego CA (US)
Revision as of 16:41, 13 July 2024 by Wikipatents (talk | contribs) (Updating Category:Jizheng_Xu_of_San_Diego_CA_(US))
Contents
Jizheng Xu of San Diego CA (US)
Executive Summary
Jizheng Xu of San Diego CA (US) is an inventor who has filed 46 patents. Their primary areas of innovation include the unit being an image region, e.g. an object (34 patents), PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION (29 patents), characterised by syntax aspects related to video coding, e.g. related to compression standards (26 patents), and they have worked with companies such as Beijing Bytedance Network Technology Co., Ltd. (38 patents), Bytedance Inc. (8 patents). Their most frequent collaborators include (46 collaborations), (38 collaborations), (30 collaborations).
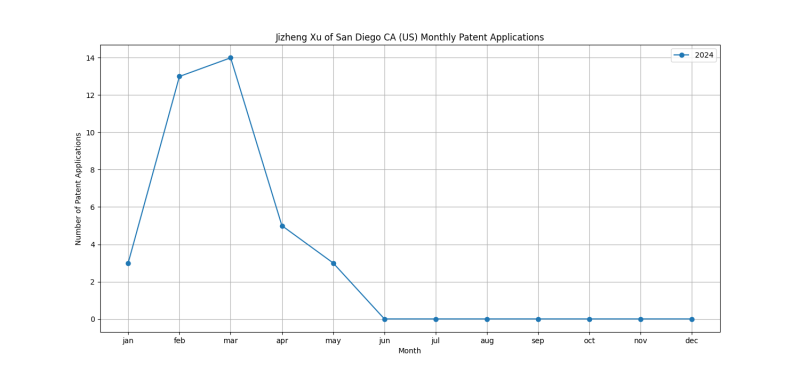
Patent Filing Activity
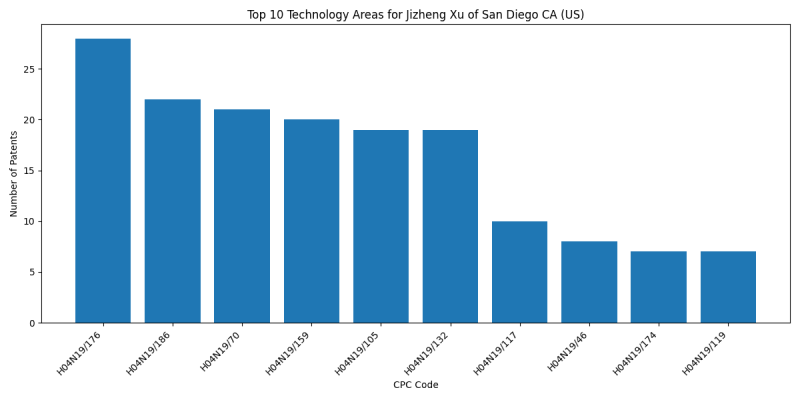
Technology Areas
List of Technology Areas
- H04N19/176 (the unit being an image region, e.g. an object): 34 patents
- H04N19/186 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 29 patents
- H04N19/70 (characterised by syntax aspects related to video coding, e.g. related to compression standards): 26 patents
- H04N19/132 (Sampling, masking or truncation of coding units, e.g. adaptive resampling, frame skipping, frame interpolation or high-frequency transform coefficient masking): 24 patents
- H04N19/159 (by monitoring actual compressed data size at the memory before deciding storage at the transmission buffer): 23 patents
- H04N19/105 (Selection of the reference unit for prediction within a chosen coding or prediction mode, e.g. adaptive choice of position and number of pixels used for prediction): 22 patents
- H04N19/117 (Filters, e.g. for pre-processing or post-processing (sub-band filter banks): 13 patents
- H04N19/119 (Adaptive subdivision aspects, e.g. subdivision of a picture into rectangular or non-rectangular coding blocks): 9 patents
- H04N19/46 (Embedding additional information in the video signal during the compression process (): 9 patents
- H04N19/174 (the region being a slice, e.g. a line of blocks or a group of blocks): 9 patents
- H04N19/593 (involving spatial prediction techniques): 8 patents
- H04N19/172 (the unit being an image region, e.g. an object): 7 patents
- H04N19/52 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 6 patents
- H04N19/96 (Tree coding, e.g. quad-tree coding): 6 patents
- H04N19/1883 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 5 patents
- H04N19/139 (Analysis of motion vectors, e.g. their magnitude, direction, variance or reliability): 5 patents
- H04N19/12 (Selection from among a plurality of transforms or standards, e.g. selection between discrete cosine transform [DCT] and sub-band transform or selection between H.263 and H.264): 5 patents
- H04N19/124 (Quantisation): 5 patents
- H04N19/157 (Assigned coding mode, i.e. the coding mode being predefined or preselected to be further used for selection of another element or parameter): 5 patents
- H04N19/184 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 5 patents
- H04N19/196 (being specially adapted for the computation of encoding parameters, e.g. by averaging previously computed encoding parameters (processing of motion vectors): 5 patents
- H04N19/137 (Motion inside a coding unit, e.g. average field, frame or block difference): 4 patents
- H04N19/82 (involving filtering within a prediction loop): 4 patents
- H04N19/60 (using transform coding): 3 patents
- H04N19/11 (among a plurality of spatial predictive coding modes): 3 patents
- H04N19/17 (the unit being an image region, e.g. an object): 2 patents
- H04N19/189 (characterised by the adaptation method, adaptation tool or adaptation type used for the adaptive coding): 2 patents
- H04N19/167 (Position within a video image, e.g. region of interest [ROI]): 2 patents
- H04N19/30 (using hierarchical techniques, e.g. scalability (): 2 patents
- H04N19/109 (among a plurality of temporal predictive coding modes): 2 patents
- H04N19/129 (Scanning of coding units, e.g. zig-zag scan of transform coefficients or flexible macroblock ordering [FMO]): 2 patents
- H04N19/188 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 2 patents
- H04N19/635 (characterised by filter definition or implementation details): 2 patents
- H04N19/86 (involving reduction of coding artifacts, e.g. of blockiness): 2 patents
- H04N19/517 (Motion estimation or motion compensation): 2 patents
- H04N19/577 (Motion compensation with bidirectional frame interpolation, i.e. using B-pictures): 2 patents
- H04N19/503 (involving temporal prediction (adaptive coding with adaptive selection between spatial and temporal predictive coding): 2 patents
- H04N19/513 (Processing of motion vectors): 2 patents
- H04N19/107 (between spatial and temporal predictive coding, e.g. picture refresh): 2 patents
- H04N19/136 (Adaptive entropy coding, e.g. adaptive variable length coding [AVLC] or context adaptive binary arithmetic coding [CABAC]): 2 patents
- G06T9/004 ({Predictors, e.g. intraframe, interframe coding}): 1 patents
- G06T11/001 ({Texturing; Colouring; Generation of texture or colour (inpainting): 1 patents
- G06T11/40 (Filling a planar surface by adding surface attributes, e.g. colour or texture): 1 patents
- G06V10/20 (IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING): 1 patents
- H04N19/463 (Embedding additional information in the video signal during the compression process (): 1 patents
- H04N19/80 (Details of filtering operations specially adapted for video compression, e.g. for pixel interpolation (): 1 patents
- H04N19/197 (using optimisation based on Lagrange multipliers): 1 patents
- H04N19/58 (Motion compensation with long-term prediction, i.e. the reference frame for a current frame not being the temporally closest one (): 1 patents
- H04N19/127 (Prioritisation of hardware or computational resources): 1 patents
- G06F17/16 (Matrix or vector computation {, e.g. matrix-matrix or matrix-vector multiplication, matrix factorization (matrix transposition): 1 patents
- H04N19/61 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 1 patents
- H04N9/67 (for matrixing (camera processing pipelines for matrixing of colour signals): 1 patents
- H04N19/521 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 1 patents
- H04N19/573 (Motion compensation with multiple frame prediction using two or more reference frames in a given prediction direction): 1 patents
- H04N19/103 (using adaptive coding): 1 patents
- H04N19/50 (using predictive coding (): 1 patents
- H04N19/51 (Motion estimation or motion compensation): 1 patents
- H04N19/14 (Coding unit complexity, e.g. amount of activity or edge presence estimation (): 1 patents
- H04N19/56 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 1 patents
- H04N19/18 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 1 patents
- H04N11/044 (using pulse code modulation {(): 1 patents
- H04N19/126 (Details of normalisation or weighting functions, e.g. normalisation matrices or variable uniform quantisers): 1 patents
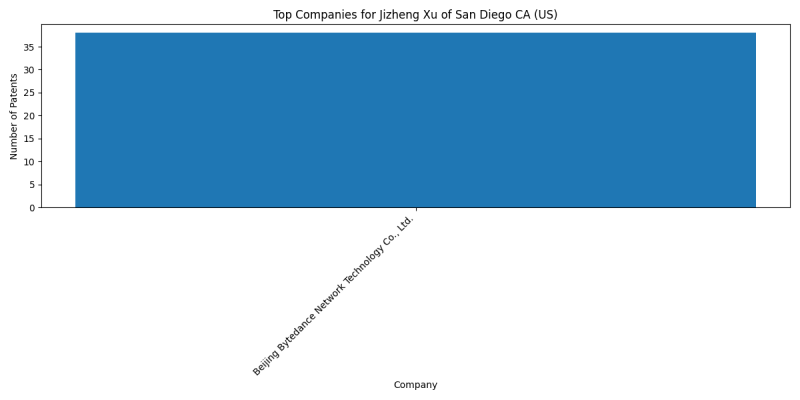
Companies
List of Companies
- Beijing Bytedance Network Technology Co., Ltd.: 38 patents
- Bytedance Inc.: 8 patents
Collaborators
- Li Zhang of San Diego CA (US) (46 collaborations)
- Kai Zhang of San Diego CA (US) (38 collaborations)
- Hongbin Liu (30 collaborations)
- Yue Wang (20 collaborations)
- Zhipin Deng (17 collaborations)
- Weijia Zhu of San Diego CA (US) (14 collaborations)
- Ye-kui Wang of San Diego CA (US) (10 collaborations)
- Yang Wang (3 collaborations)
- Hsiao Chiang Chuang of San Diego CA (US) (2 collaborations)
- Ye-Kui Wang of San Diego CA (US) (2 collaborations)
- Kai ZHANG of San Diego CA (US) (1 collaborations)
- Kui Fan of San Diego CA (US) (1 collaborations)
Subcategories
This category has the following 10 subcategories, out of 10 total.
H
J
K
L
W
Y
Z
Pages in category "Jizheng Xu of San Diego CA (US)"
The following 9 pages are in this category, out of 9 total.
1
- 18511098. MOTION VECTOR RANGE BASED ON MOTION VECTOR PRECISION simplified abstract (BEIJING BYTEDANCE NETWORK TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.)
- 18511098. MOTION VECTOR RANGE BASED ON MOTION VECTOR PRECISION simplified abstract (Bytedance Inc.)
- 18515482. WEIGHTED SAMPLE BI-PREDICTION IN VIDEO CODING simplified abstract (BEIJING BYTEDANCE NETWORK TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.)
- 18515482. WEIGHTED SAMPLE BI-PREDICTION IN VIDEO CODING simplified abstract (Bytedance Inc.)
- 18516493. Use Of Header Syntax Elements And Adaptation Parameter Set simplified abstract (BEIJING BYTEDANCE NETWORK TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.)
- 18516493. Use Of Header Syntax Elements And Adaptation Parameter Set simplified abstract (Bytedance Inc.)
- 18675843. CHROMA DEBLOCKING HARMONIZATION FOR VIDEO CODING simplified abstract (Beijing Bytedance Network Technology Co., Ltd.)
- 18813993. POSITION-DEPENDENT INTRA PREDICTION SAMPLE FILTERING (Beijing Bytedance Network Technology Co., Ltd.)
- 18813993. POSITION-DEPENDENT INTRA PREDICTION SAMPLE FILTERING (ByteDance Inc.)
Categories:
- Li Zhang of San Diego CA (US)
- Kai Zhang of San Diego CA (US)
- Hongbin Liu
- Yue Wang
- Zhipin Deng
- Weijia Zhu of San Diego CA (US)
- Ye-kui Wang of San Diego CA (US)
- Yang Wang
- Hsiao Chiang Chuang of San Diego CA (US)
- Ye-Kui Wang of San Diego CA (US)
- Kai ZHANG of San Diego CA (US)
- Kui Fan of San Diego CA (US)
- Jizheng Xu of San Diego CA (US)
- Inventors
- Inventors filing patents with Bytedance Inc.
- Inventors filing patents with Beijing Bytedance Network Technology Co., Ltd.