Category:Ye-kui Wang of San Diego CA (US)
Revision as of 16:41, 13 July 2024 by Wikipatents (talk | contribs) (Updating Category:Ye-kui_Wang_of_San_Diego_CA_(US))
Contents
Ye-kui Wang of San Diego CA (US)
Executive Summary
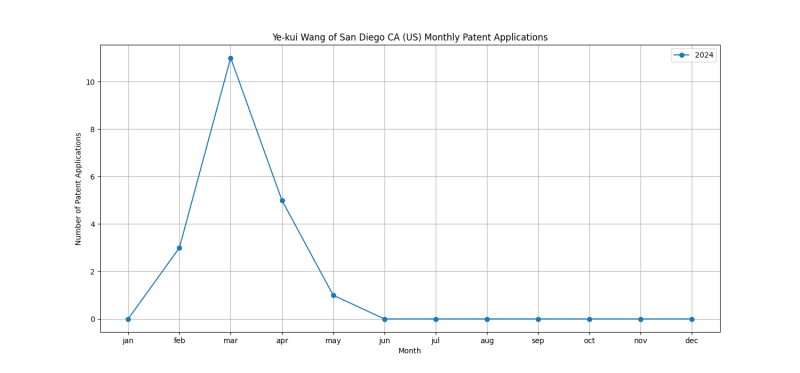
Ye-kui Wang of San Diego CA (US) is an inventor who has filed 51 patents. Their primary areas of innovation include characterised by syntax aspects related to video coding, e.g. related to compression standards (44 patents), the unit being an image region, e.g. an object (28 patents), the region being a slice, e.g. a line of blocks or a group of blocks (28 patents), and they have worked with companies such as Bytedance Inc. (31 patents), Beijing Bytedance Network Technology Co., Ltd. (20 patents). Their most frequent collaborators include (33 collaborations), (24 collaborations), (19 collaborations).
Patent Filing Activity
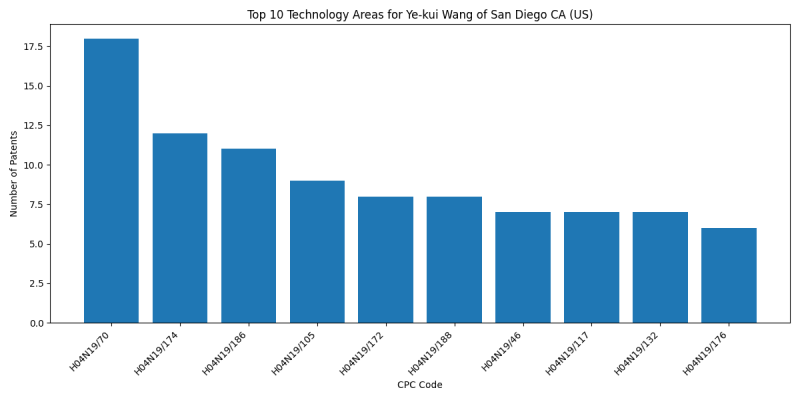
Technology Areas
List of Technology Areas
- H04N19/70 (characterised by syntax aspects related to video coding, e.g. related to compression standards): 44 patents
- H04N19/172 (the unit being an image region, e.g. an object): 28 patents
- H04N19/174 (the region being a slice, e.g. a line of blocks or a group of blocks): 28 patents
- H04N19/188 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 25 patents
- H04N19/105 (Selection of the reference unit for prediction within a chosen coding or prediction mode, e.g. adaptive choice of position and number of pixels used for prediction): 24 patents
- H04N19/46 (Embedding additional information in the video signal during the compression process (): 21 patents
- H04N19/186 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 16 patents
- H04N19/184 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 12 patents
- H04N19/132 (Sampling, masking or truncation of coding units, e.g. adaptive resampling, frame skipping, frame interpolation or high-frequency transform coefficient masking): 10 patents
- H04N19/176 (the unit being an image region, e.g. an object): 9 patents
- H04N19/30 (using hierarchical techniques, e.g. scalability (): 9 patents
- H04N19/117 (Filters, e.g. for pre-processing or post-processing (sub-band filter banks): 9 patents
- H04N19/136 (Adaptive entropy coding, e.g. adaptive variable length coding [AVLC] or context adaptive binary arithmetic coding [CABAC]): 6 patents
- H04N19/159 (by monitoring actual compressed data size at the memory before deciding storage at the transmission buffer): 6 patents
- H04N19/82 (involving filtering within a prediction loop): 5 patents
- H04N19/119 (Adaptive subdivision aspects, e.g. subdivision of a picture into rectangular or non-rectangular coding blocks): 4 patents
- H04N19/96 (Tree coding, e.g. quad-tree coding): 4 patents
- H04N19/187 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 4 patents
- H04N19/1883 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 3 patents
- H04N19/157 (Assigned coding mode, i.e. the coding mode being predefined or preselected to be further used for selection of another element or parameter): 3 patents
- H04N19/423 (characterised by memory arrangements (): 3 patents
- H04N19/44 (Decoders specially adapted therefor, e.g. video decoders which are asymmetric with respect to the encoder): 3 patents
- H04N19/139 (Analysis of motion vectors, e.g. their magnitude, direction, variance or reliability): 3 patents
- H04N19/167 (Position within a video image, e.g. region of interest [ROI]): 3 patents
- H04N19/196 (being specially adapted for the computation of encoding parameters, e.g. by averaging previously computed encoding parameters (processing of motion vectors): 3 patents
- H04N19/31 (in the temporal domain): 3 patents
- H04N19/103 (using adaptive coding): 2 patents
- H04N19/52 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 2 patents
- H04N19/635 (characterised by filter definition or implementation details): 2 patents
- H04N19/12 (Selection from among a plurality of transforms or standards, e.g. selection between discrete cosine transform [DCT] and sub-band transform or selection between H.263 and H.264): 2 patents
- H04N19/18 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 2 patents
- H04N19/109 (among a plurality of temporal predictive coding modes): 2 patents
- H04N19/503 (involving temporal prediction (adaptive coding with adaptive selection between spatial and temporal predictive coding): 2 patents
- H04N19/134 (characterised by the element, parameter or criterion affecting or controlling the adaptive coding): 1 patents
- H04N19/88 (involving rearrangement of data among different coding units, e.g. shuffling, interleaving, scrambling or permutation of pixel data or permutation of transform coefficient data among different blocks): 1 patents
- H04N19/593 (involving spatial prediction techniques): 1 patents
- H04N19/91 (Entropy coding, e.g. variable length coding [VLC] or arithmetic coding): 1 patents
- H04N19/547 (using feature points or meshes): 1 patents
- H04N19/573 (Motion compensation with multiple frame prediction using two or more reference frames in a given prediction direction): 1 patents
- H04N19/463 (Embedding additional information in the video signal during the compression process (): 1 patents
- H04N19/80 (Details of filtering operations specially adapted for video compression, e.g. for pixel interpolation (): 1 patents
- H04N19/152 (by measuring the fullness of the transmission buffer): 1 patents
- H04N19/146 (Data rate or code amount at the encoder output): 1 patents
- H04N19/189 (characterised by the adaptation method, adaptation tool or adaptation type used for the adaptive coding): 1 patents
- H04N19/197 (using optimisation based on Lagrange multipliers): 1 patents
- H04N19/58 (Motion compensation with long-term prediction, i.e. the reference frame for a current frame not being the temporally closest one (): 1 patents
- H04N19/86 (involving reduction of coding artifacts, e.g. of blockiness): 1 patents
- H04N19/127 (Prioritisation of hardware or computational resources): 1 patents
- H04N19/85 (using pre-processing or post-processing specially adapted for video compression): 1 patents
- H04N19/60 (using transform coding): 1 patents
- H04N19/42 (characterised by implementation details or hardware specially adapted for video compression or decompression, e.g. dedicated software implementation (): 1 patents
- H04N19/107 (between spatial and temporal predictive coding, e.g. picture refresh): 1 patents
- H04N19/11 (among a plurality of spatial predictive coding modes): 1 patents
- H04N19/122 (Selection of transform size, e.g. 8x8 or 2x4x8 DCT; Selection of sub-band transforms of varying structure or type): 1 patents
- H04N19/61 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 1 patents
- H04N19/182 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 1 patents
- H04N19/597 (specially adapted for multi-view video sequence encoding): 1 patents
- H04N19/433 (PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION): 1 patents
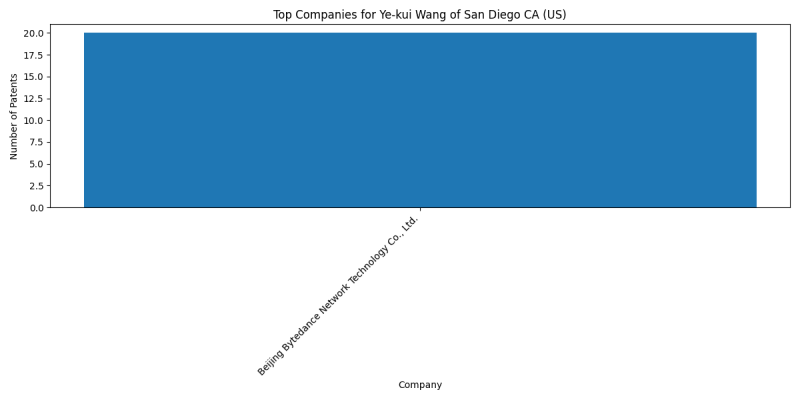
Companies
List of Companies
- Bytedance Inc.: 31 patents
- Beijing Bytedance Network Technology Co., Ltd.: 20 patents
Collaborators
- Li Zhang of San Diego CA (US) (33 collaborations)
- Kai Zhang of San Diego CA (US) (24 collaborations)
- Zhipin Deng (19 collaborations)
- Jizheng Xu of San Diego CA (US) (10 collaborations)
- Hongbin Liu (4 collaborations)
- Kui Fan of San Diego CA (US) (3 collaborations)
- Weijia Zhu of San Diego CA (US) (3 collaborations)
- Yang Wang (2 collaborations)
- Kai Zhang of Los Angeles CA (US) (1 collaborations)
- Yue Wang (1 collaborations)
Subcategories
This category has the following 9 subcategories, out of 9 total.
H
J
K
L
W
Y
Z
Pages in category "Ye-kui Wang of San Diego CA (US)"
The following 12 pages are in this category, out of 12 total.
1
- 18516468. SUBPICTURE SUB-BITSTREAM EXTRACTION PROCESS ENHANCEMENTS simplified abstract (Bytedance Inc.)
- 18516493. Use Of Header Syntax Elements And Adaptation Parameter Set simplified abstract (BEIJING BYTEDANCE NETWORK TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.)
- 18516493. Use Of Header Syntax Elements And Adaptation Parameter Set simplified abstract (Bytedance Inc.)
- 18516654. INTRA RANDOM ACCESS POINTS FOR PICTURE CODING simplified abstract (Bytedance Inc.)
- 18517283. Signaling Of Subpicture Level And Buffering Information simplified abstract (Bytedance Inc.)
- 18517328. Signaling Of Gradual Decoding Refresh And Reference Picture Lists simplified abstract (Bytedance Inc.)
- 18517737. Coefficients Coding In Transform Skip Mode simplified abstract (BEIJING BYTEDANCE NETWORK TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.)
- 18517737. Coefficients Coding In Transform Skip Mode simplified abstract (Bytedance Inc.)
- 18520196. Scalable Nesting Of Supplemental Enhancement Information Messages In Video Coding simplified abstract (Bytedance Inc.)
- 18526640. COMBINATION OF SUBPICTURES AND SCALABILITY simplified abstract (Beijing Bytedance Network Technology Co., Ltd.)
Categories:
- Li Zhang of San Diego CA (US)
- Kai Zhang of San Diego CA (US)
- Zhipin Deng
- Jizheng Xu of San Diego CA (US)
- Hongbin Liu
- Kui Fan of San Diego CA (US)
- Weijia Zhu of San Diego CA (US)
- Yang Wang
- Kai Zhang of Los Angeles CA (US)
- Yue Wang
- Ye-kui Wang of San Diego CA (US)
- Inventors
- Inventors filing patents with Beijing Bytedance Network Technology Co., Ltd.
- Inventors filing patents with Bytedance Inc.