Apple Patent Applications: Difference between revisions
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Apple's Patent | == Apple's Patent Filings in Technology Areas == | ||
Apple | |||
Given that it takes a few years to get patents granted for these, we can expect Apple to release more devices and features along these lines in the next 2 to 4 years. | |||
Apple's patent filings in 2024 reveal a strong focus on these broad tech areas: | |||
1. Digital data processing (G06F) leads the pack, hinting at major software and interface innovations. | |||
2. Wireless tech (H04W) is a close second, likely advancing 5G and other communication protocols. | |||
3. Image processing (G06T) suggests continued push in graphics, possibly for AR/VR applications. | |||
4. Digital information transmission (H04L) points to improvements in network security and protocols. | |||
5. Video communication tech (H04N) indicates upgrades to camera and display systems. | |||
6. Optical tech (G02B) could be tied to camera improvements or AR hardware development. | |||
7. Display tech (G09G) remains a priority, potentially for next-gen screens. | |||
8. Semiconductor work (H01L) aligns with Apple's custom chip strategy. | |||
9. Transmission systems (H04B) suggest ongoing refinement of data transfer tech. | |||
10. Health-related tech (A61B) hints at expanding wellness features, likely for wearables. | |||
Apple's patent activity, this year so far, shows a balanced approach, enhancing core technologies while pushing into emerging fields like AR and health tech. | |||
[[File:Screenshot 2024-06-26 at 4.41.26 PM.png|thumb|Apple's technology patent applications by technology area in 2024 up to May 2024]] | |||
Drilling down into the patent applications by Apple this year. These are the specific (sub technologies) areas that they have been filing in the most: | |||
We're seeing spikes in March across multiple tech areas | |||
From AI to wearables, Apple seems to be pushing boundaries in various domains. | |||
The question is: which of these technology areas will they actually be pushing in their future products? 🤔 | |||
What area are you most excited about? AR glasses? Foldable devices? Health tech? | |||
(These are sub-codes so it gets a bit nerdy here) | |||
G06F3/013: Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Interface arrangements associated with the keyboard or the like. | |||
G06F3/0482: Digital input from handwriting recognition. | |||
G06F3/04842: Digital input from touch screens. | |||
G06F3/017: Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer. | |||
G06F3/04815: Digital input from physical keyboard or key actuation devices. | |||
G06F3/04883: Digital input using optical detection of user movements. | |||
G06T19/006: Image data processing or generation, in general. | |||
G06F3/0488: Digital input using detection of user movements. | |||
G02B27/0172: Optical systems or apparatus not provided for by any of the groups G02B1/00- | |||
G02B26/00, for imaging purposes. | |||
H04L5/0051: Arrangements affording multiple use of the transmission path. | |||
== Introduction to Apple's Patent Portfolio == | |||
Apple Inc., a leader in technology innovation, implements a robust patent application strategy, filing up to 100 patents weekly. This strategic approach not only protects its intellectual property but also fortifies its position in the competitive tech landscape. | |||
See the following page to get a summary of Apple's weekly patent applications: [[Weekly updates on Apple's Patent Applications]]. | See the following page to get a summary of Apple's weekly patent applications: [[Weekly updates on Apple's Patent Applications]]. | ||
== Apple Patents of Interest == | == Apple Patents of Interest == | ||
[[US Patent Application 20230225659. Biosignal Sensing Device Using Dynamic Selection Of Electrodes]]. In layman's terms: A device that picks the best sensors, on the fly, to read body signals. | === Highlighted Apple Patent: Biosignal Sensing Device === | ||
One noteworthy example is the US Patent Application 20230225659, concerning a biosignal sensing device. This invention dynamically selects electrodes to optimize the reading of body signals, showcasing Apple's commitment to innovation in health technology: [[US Patent Application 20230225659. Biosignal Sensing Device Using Dynamic Selection Of Electrodes]]. | |||
In layman's terms: A device that picks the best sensors, on the fly, to read body signals. | |||
== About Apple's Patent Strategy == | == About Apple's Patent Application Strategy == | ||
Apple | ===The Essence of Apple's Patent Strategy=== | ||
At the heart of Apple's success is a carefully crafted patent application strategy, ensuring its innovations like the iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch not only set new industry standards but are also legally protected worldwide. This section explores the key pillars of Apple's approach to patents, highlighting its strategic filings, balance of defensive and offensive patents, and global reach. | |||
=== Understanding Apple's Patent Strategy === | === Understanding Apple's Patent Strategy === | ||
| Line 21: | Line 90: | ||
=== Innovation First, Patents Second: === | === Innovation First, Patents Second: === | ||
Apple's patent strategy revolves around innovation as its foundation. The company places a strong emphasis on creating groundbreaking products and services that disrupt existing markets and set new standards. From the iconic iPhone to the revolutionary iPad and Apple Watch, each innovation is meticulously designed and developed to solve real-world problems while pushing technological boundaries. | Apple's patent strategy revolves around innovation as its foundation. The company places a strong emphasis on creating groundbreaking products and services that disrupt existing markets and set new standards. From the iconic iPhone to the revolutionary iPad and Apple Watch, each innovation is meticulously designed and developed to solve real-world problems while pushing technological boundaries. | ||
Innovation leads Apple's patent strategy, with the company focusing on groundbreaking technologies that offer real-world solutions. Apple's methodical approach to patent filing emphasizes the importance of protecting significant advancements, thereby enhancing the quality of its patent portfolio. | |||
=== Strategic Patent Filing: === | === Strategic Patent Filing: === | ||
Apple's approach to patent filing is methodical. The company carefully selects which innovations to patent, focusing on those that truly represent significant advancements. This strategy prevents the patenting of trivial or obvious features, strengthening the overall quality and credibility of its patent portfolio. | Apple's approach to patent filing is methodical. The company carefully selects which innovations to patent, focusing on those that truly represent significant advancements. This strategy prevents the patenting of trivial or obvious features, strengthening the overall quality and credibility of its patent portfolio. | ||
=== | === Defensive and Offensive Patent Balance === | ||
Apple expertly navigates the balance between defensive patents, which protect against litigation, and offensive patents, which offer negotiation leverage. This strategy is pivotal in maintaining Apple's competitive edge and fostering industry partnerships. | |||
Apple maintains a delicate balance between defensive and offensive patents. Defensive patents act as a shield against potential litigation from competitors, deterring infringement claims. Offensive patents, on the other hand, provide Apple with leverage to negotiate licensing agreements, collaborations, and partnerships with other companies. | Apple maintains a delicate balance between defensive and offensive patents. Defensive patents act as a shield against potential litigation from competitors, deterring infringement claims. Offensive patents, on the other hand, provide Apple with leverage to negotiate licensing agreements, collaborations, and partnerships with other companies. | ||
=== Global Reach | In essence, the primary objective of Apple's patent strategy is to protect its technological advancements, deter litigation, and facilitate partnerships and collaborations in the tech industry. | ||
====As a defensive strategy==== | |||
For example, as a defensive patent strategy, Apple has patented several aspects of its iPhone's design and user interface, preventing competitors from creating similar products. These defensive patents act as a deterrent against lawsuits, as competitors are aware of the legal challenges they might face if they infringe on Apple's patents. | |||
====As an offensive strategy==== | |||
Apple's legal battle with Samsung over smartphone patents is a prime example of the company using offensive patents. Apple successfully argued that Samsung infringed on several of its patents related to design and functionality, leading to a significant legal victory that underscored the strength of Apple's patent portfolio. | |||
=== Global Reach === | |||
Apple's innovations have a global impact, and its patent strategy reflects this. The company files for patents in key markets worldwide, ensuring comprehensive protection for its inventions across diverse legal jurisdictions. This strategy bolsters Apple's ability to enforce its patents and maintain a strong position in international markets. | Apple's innovations have a global impact, and its patent strategy reflects this. The company files for patents in key markets worldwide, ensuring comprehensive protection for its inventions across diverse legal jurisdictions. This strategy bolsters Apple's ability to enforce its patents and maintain a strong position in international markets. | ||
Latest revision as of 09:17, 27 September 2024
Apple's Patent Filings in Technology Areas
Given that it takes a few years to get patents granted for these, we can expect Apple to release more devices and features along these lines in the next 2 to 4 years.
Apple's patent filings in 2024 reveal a strong focus on these broad tech areas:
1. Digital data processing (G06F) leads the pack, hinting at major software and interface innovations.
2. Wireless tech (H04W) is a close second, likely advancing 5G and other communication protocols.
3. Image processing (G06T) suggests continued push in graphics, possibly for AR/VR applications.
4. Digital information transmission (H04L) points to improvements in network security and protocols.
5. Video communication tech (H04N) indicates upgrades to camera and display systems.
6. Optical tech (G02B) could be tied to camera improvements or AR hardware development.
7. Display tech (G09G) remains a priority, potentially for next-gen screens.
8. Semiconductor work (H01L) aligns with Apple's custom chip strategy.
9. Transmission systems (H04B) suggest ongoing refinement of data transfer tech.
10. Health-related tech (A61B) hints at expanding wellness features, likely for wearables.
Apple's patent activity, this year so far, shows a balanced approach, enhancing core technologies while pushing into emerging fields like AR and health tech.
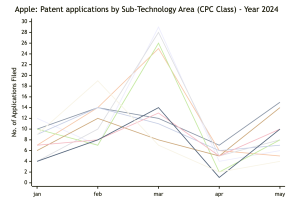
Drilling down into the patent applications by Apple this year. These are the specific (sub technologies) areas that they have been filing in the most:
We're seeing spikes in March across multiple tech areas
From AI to wearables, Apple seems to be pushing boundaries in various domains.
The question is: which of these technology areas will they actually be pushing in their future products? 🤔
What area are you most excited about? AR glasses? Foldable devices? Health tech?
(These are sub-codes so it gets a bit nerdy here)
G06F3/013: Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Interface arrangements associated with the keyboard or the like.
G06F3/0482: Digital input from handwriting recognition.
G06F3/04842: Digital input from touch screens.
G06F3/017: Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer.
G06F3/04815: Digital input from physical keyboard or key actuation devices.
G06F3/04883: Digital input using optical detection of user movements.
G06T19/006: Image data processing or generation, in general.
G06F3/0488: Digital input using detection of user movements.
G02B27/0172: Optical systems or apparatus not provided for by any of the groups G02B1/00- G02B26/00, for imaging purposes.
H04L5/0051: Arrangements affording multiple use of the transmission path.
Introduction to Apple's Patent Portfolio
Apple Inc., a leader in technology innovation, implements a robust patent application strategy, filing up to 100 patents weekly. This strategic approach not only protects its intellectual property but also fortifies its position in the competitive tech landscape.
See the following page to get a summary of Apple's weekly patent applications: Weekly updates on Apple's Patent Applications.
Apple Patents of Interest
Highlighted Apple Patent: Biosignal Sensing Device
One noteworthy example is the US Patent Application 20230225659, concerning a biosignal sensing device. This invention dynamically selects electrodes to optimize the reading of body signals, showcasing Apple's commitment to innovation in health technology: US Patent Application 20230225659. Biosignal Sensing Device Using Dynamic Selection Of Electrodes.
In layman's terms: A device that picks the best sensors, on the fly, to read body signals.
About Apple's Patent Application Strategy
The Essence of Apple's Patent Strategy
At the heart of Apple's success is a carefully crafted patent application strategy, ensuring its innovations like the iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch not only set new industry standards but are also legally protected worldwide. This section explores the key pillars of Apple's approach to patents, highlighting its strategic filings, balance of defensive and offensive patents, and global reach.
Understanding Apple's Patent Strategy
Apple's patent strategy is a multi-faceted approach that combines innovation, legal expertise, and market positioning. At its core, this strategy aims to establish a competitive edge, defend against potential threats, and foster an environment conducive to creativity and technological advancement. Let's explore the key aspects of Apple's patent strategy:
Innovation First, Patents Second:
Apple's patent strategy revolves around innovation as its foundation. The company places a strong emphasis on creating groundbreaking products and services that disrupt existing markets and set new standards. From the iconic iPhone to the revolutionary iPad and Apple Watch, each innovation is meticulously designed and developed to solve real-world problems while pushing technological boundaries.
Innovation leads Apple's patent strategy, with the company focusing on groundbreaking technologies that offer real-world solutions. Apple's methodical approach to patent filing emphasizes the importance of protecting significant advancements, thereby enhancing the quality of its patent portfolio.
Strategic Patent Filing:
Apple's approach to patent filing is methodical. The company carefully selects which innovations to patent, focusing on those that truly represent significant advancements. This strategy prevents the patenting of trivial or obvious features, strengthening the overall quality and credibility of its patent portfolio.
Defensive and Offensive Patent Balance
Apple expertly navigates the balance between defensive patents, which protect against litigation, and offensive patents, which offer negotiation leverage. This strategy is pivotal in maintaining Apple's competitive edge and fostering industry partnerships.
Apple maintains a delicate balance between defensive and offensive patents. Defensive patents act as a shield against potential litigation from competitors, deterring infringement claims. Offensive patents, on the other hand, provide Apple with leverage to negotiate licensing agreements, collaborations, and partnerships with other companies.
In essence, the primary objective of Apple's patent strategy is to protect its technological advancements, deter litigation, and facilitate partnerships and collaborations in the tech industry.
As a defensive strategy
For example, as a defensive patent strategy, Apple has patented several aspects of its iPhone's design and user interface, preventing competitors from creating similar products. These defensive patents act as a deterrent against lawsuits, as competitors are aware of the legal challenges they might face if they infringe on Apple's patents.
As an offensive strategy
Apple's legal battle with Samsung over smartphone patents is a prime example of the company using offensive patents. Apple successfully argued that Samsung infringed on several of its patents related to design and functionality, leading to a significant legal victory that underscored the strength of Apple's patent portfolio.
Global Reach
Apple's innovations have a global impact, and its patent strategy reflects this. The company files for patents in key markets worldwide, ensuring comprehensive protection for its inventions across diverse legal jurisdictions. This strategy bolsters Apple's ability to enforce its patents and maintain a strong position in international markets.
Maintaining Trade Secrets:
While patents offer protection, not all innovations are disclosed through them. Apple strategically keeps certain technologies and processes as trade secrets. This provides an added layer of security, as trade secrets are not publicly disclosed, making it challenging for competitors to replicate or reverse-engineer Apple's proprietary innovations.
Litigation and Settlements:
Apple has been involved in various high-profile patent disputes over the years. These legal battles showcase the company's commitment to defending its intellectual property vigorously. However, Apple also acknowledges the benefits of settling certain disputes out of court, as protracted legal battles can be resource-intensive and may divert focus from innovation.
Impact and Implications
Apple's patent strategy has far-reaching implications for the technology industry:
Elevating Industry Standards:
By setting high standards for patent quality, Apple encourages other companies to innovate genuinely and contribute to the advancement of technology. This leads to a healthier and more competitive industry landscape.
Innovation Ecosystem:
Apple's patent strategy fosters an environment that nurtures innovation. Startups and smaller tech firms may draw inspiration from Apple's approach, encouraging them to prioritize originality and protect their inventions.
Legal Precedent:
Apple's involvement in patent litigation has contributed to shaping legal precedents in intellectual property law. Its cases often serve as benchmarks for future disputes and guide the industry on patent-related matters.
Market Dominance and Consumer Trust:
The meticulous attention to detail in Apple's products, fueled by its patent strategy, contributes to its reputation for quality and reliability. This, in turn, helps the company maintain consumer trust and loyalty.
Apple's patent strategy is a masterclass in how a technology giant can effectively navigate the intricate landscape of innovation and intellectual property protection. By prioritizing genuine innovation, strategically patenting key technologies, and balancing defensive and offensive patent approaches, Apple has solidified its position as an industry leader. The company's commitment to pushing the boundaries of technology while safeguarding its inventions underscores the significance of a well-crafted patent strategy in a rapidly evolving tech world. As Apple continues to innovate and inspire, its patent strategy will undoubtedly remain a cornerstone of its success.
How does Apple decide which innovations to keep as trade secrets instead of patenting?
Apple evaluates the nature of its innovations and their strategic importance to determine whether to patent them or keep them as trade secrets. Innovations that offer a competitive advantage and can be effectively protected without disclosure might be kept as trade secrets. This decision is influenced by factors such as the ease of reverse engineering, the ability to maintain secrecy, and the legal protections available in different jurisdictions.
What specific technologies or innovations has Apple decided to keep as trade secrets?
While specific details about Apple's trade secrets are, by nature, not publicly disclosed, it generally includes proprietary technologies and processes integral to Apple's products and services that offer a significant competitive advantage. This could encompass unique manufacturing techniques, algorithms, and software processes that are central to the user experience but not visible or patentable in a traditional sense.
How does Apple's global patent strategy vary by region, and what are the challenges it faces in different jurisdictions?
Apple's global patent strategy involves tailoring its approach to the legal and market conditions of each region. Challenges vary, including differences in patent law, the speed and cost of patent approval, and the effectiveness of enforcement. In some jurisdictions, Apple may prioritize certain types of patents or adopt different strategies for litigation and licensing to navigate these challenges effectively.
How does Apple balance its patent portfolio between hardware and software innovations?
Apple maintains a balanced patent portfolio by strategically patenting both hardware and software innovations. The company assesses the importance of each innovation in its overall ecosystem, focusing on those that enhance user experience, offer new functionalities, or represent significant technical advancements. This balance helps Apple protect and leverage its diverse range of products and services.
What role do partnerships and collaborations play in Apple's patent strategy?
Partnerships and collaborations are an essential part of Apple's patent strategy. Through strategic alliances, Apple can access complementary technologies, share the cost and risk of innovation, and expand its intellectual property portfolio. Collaborations can also lead to cross-licensing agreements, allowing Apple to use patents owned by other companies while sharing its own, thereby fostering innovation and reducing the risk of litigation.
How has Apple's approach to patent litigation evolved over the years, and what factors influence its decision to settle disputes out of court?
Apple's approach to patent litigation has evolved to become more strategic, focusing on protecting its core technologies and deterring infringement. The decision to settle disputes out of court is influenced by several factors, including the potential cost and duration of litigation, the strength of Apple's legal position, and the impact on its business and innovation agenda. Settling allows Apple to avoid lengthy legal battles, saving resources that can be redirected towards innovation and product development.